This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by Keyur Modi
In this project, I’ve developed a scalable, serverless photo-sharing application leveraging various AWS services. This application demonstrates a modern, cloud-native approach to building robust, secure, and cost-effective solutions for storing, processing, and sharing photos.
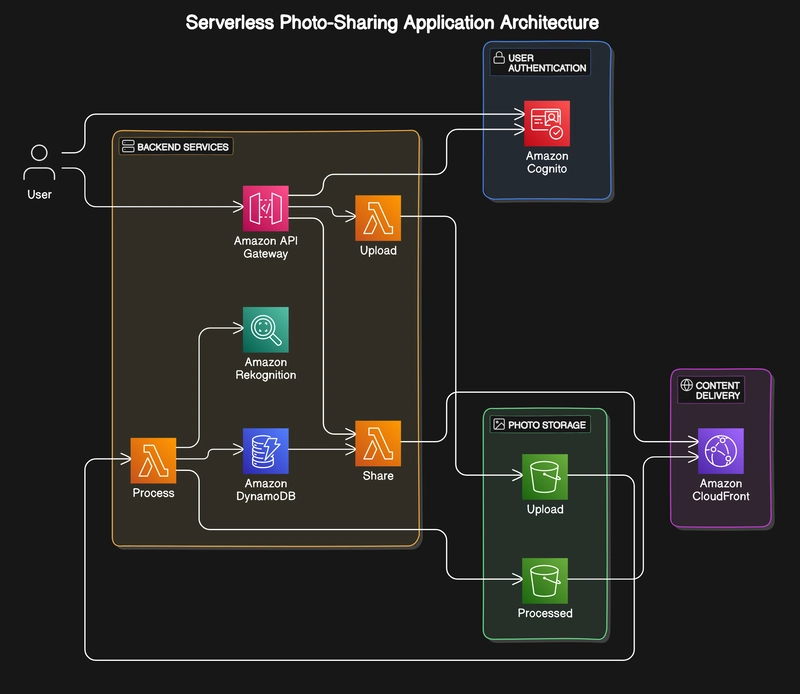
Architecture Overview
The application utilizes the following AWS services:
- Amazon Cognito for user authentication
- Amazon API Gateway for API management
- AWS Lambda for serverless compute
- Amazon S3 for photo storage
- Amazon DynamoDB for metadata storage
- Amazon CloudFront for content delivery
- Amazon Rekognition for image analysis (optional)
Detailed Component Breakdown
1. User Authentication (Amazon Cognito)
- Implements secure user sign-up, sign-in, and account management
- Provides token-based authentication for API access
- Supports social identity providers for enhanced user experience
2. API Management (Amazon API Gateway)
- Manages RESTful API endpoints for the application
- Integrates directly with Lambda functions
- Implements API key management and usage plans for rate limiting
3. Serverless Compute (AWS Lambda)
Three main Lambda functions handle core functionality:
a) Upload Handler:
— Processes incoming photos
— Stores original photos in S3
— Records metadata in DynamoDB
b) Thumbnail Generator:
— Triggered by S3 events on new uploads
— Creates resized versions of uploaded images
— Stores thumbnails back in S3
c) Sharing Handler:
— Generates and manages sharing URLs
— Creates signed URLs for secure, time-limited access
4. Photo Storage (Amazon S3)
- Scalable object storage for original photos and processed versions
- Configured with appropriate lifecycle policies for cost optimization
- Versioning enabled for data protection and recovery
5. Metadata Storage (Amazon DynamoDB)
- NoSQL database storing photo metadata (user ID, timestamps, sharing status)
- Supports high-throughput read/write operations
- Utilizes Global Secondary Indexes for efficient querying
6. Content Delivery (Amazon CloudFront)
- Global CDN for fast and secure delivery of photos
- Edge caching to reduce latency and backend load
- HTTPS enforcement and signed URLs for secure access to shared photos
7. Image Analysis (Amazon Rekognition) — Optional
- AI-powered image recognition for auto-tagging and content moderation
- Integrated with the upload workflow for real-time processing
Implementation Guide
Step 1: Set Up User Authentication
- Open the Amazon Cognito console
- Create a new User Pool — Configure sign-in options (email, username) — Set password policies — Enable Multi-Factor Authentication if desired
- Create an App Client for your application
- Note the User Pool ID and App Client ID
Step 2: Create S3 Buckets
- Open the Amazon S3 console
- Create two buckets:
—
original-photos-bucket—processed-photos-bucket - Configure CORS on both buckets
- Set up lifecycle rules for cost optimization
Step 3: Set Up DynamoDB
- Create a new table named
PhotoMetadata - Set primary key as
photoId(String) - Add a Global Secondary Index on
userId - Enable DynamoDB Streams for real-time processing
Step 4: Create Lambda Functions
Create the following Lambda functions:
P.S. this is a basic code
a) uploadHandler:
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const s3 = new AWS.S3();
const dynamo = new AWS.DynamoDB.DocumentClient();
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const body = JSON.parse(event.body);
const photoId = generateUniqueId();
const userId = event.requestContext.authorizer.claims.sub;
// Upload to S3
await s3.putObject({
Bucket: 'original-photos-bucket',
Key: `${userId}/${photoId}`,
Body: Buffer.from(body.image, 'base64'),
ContentType: 'image/jpeg'
}).promise();
// Save metadata to DynamoDB
await dynamo.put({
TableName: 'PhotoMetadata',
Item: {
photoId: photoId,
userId: userId,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
}
}).promise();
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({ photoId: photoId })
};
};
b) thumbnailGenerator:
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const sharp = require('sharp');
const s3 = new AWS.S3();
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const bucket = event.Records[0].s3.bucket.name;
const key = decodeURIComponent(event.Records[0].s3.object.key.replace(/\+/g, " "));
const image = await s3.getObject({ Bucket: bucket, Key: key }).promise();
const resizedImage = await sharp(image.Body)
.resize(200, 200, { fit: 'inside' })
.toBuffer();
await s3.putObject({
Bucket: 'processed-photos-bucket',
Key: `thumbnails/${key}`,
Body: resizedImage,
ContentType: 'image/jpeg'
}).promise();
};
c) shareHandler:
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const dynamo = new AWS.DynamoDB.DocumentClient();
const cloudFront = new AWS.CloudFront.Signer(process.env.CF_KEY_PAIR_ID, process.env.CF_PRIVATE_KEY);
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const photoId = event.pathParameters.photoId;
const userId = event.requestContext.authorizer.claims.sub;
// Verify ownership
const result = await dynamo.get({
TableName: 'PhotoMetadata',
Key: { photoId: photoId }
}).promise();
if (result.Item.userId !== userId) {
return { statusCode: 403, body: 'Access denied' };
}
// Generate signed URL
const url = cloudFront.getSignedUrl({
url: https://your-cf-distribution.cloudfront.net/${photoId},
expires: Math.floor((Date.now() + 86400000) / 1000) // 24 hours from now
});
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({ url: url })
};
};
Step 5: Configure API Gateway
- Create a new REST API
- Set up resources and methods: — POST /photos (for uploads) — GET /photos (for listing user’s photos) — POST /photos/{photoId}/share (for sharing)
- Integrate each endpoint with the corresponding Lambda function
- Enable CORS and deploy the API
Step 6: Set Up CloudFront
- Create a new Web distribution
- Set Origin to your processed-photos S3 bucket
- Configure Viewer Protocol Policy to redirect HTTP to HTTPS
- Restrict Bucket Access and create a new Origin Access Identity
- Update the S3 bucket policy to allow access from the CloudFront OAI
Step 7: Integrate Amazon Rekognition (Optional)
- Update the
uploadHandlerLambda function to call Rekognition for image analysis - Store the resulting tags in the DynamoDB metadata
Step 8: Frontend Development
- Create a web application using React or Vue.js
- Implement user authentication flow using Amazon Cognito SDK
- Develop UI for photo upload, gallery view, and sharing functionality
- Integrate with your API Gateway endpoints for backend operations
Security Considerations
- Implement least privilege access for all IAM roles
- Use Cognito User Pools for secure user authentication
- Encrypt data at rest in S3 and DynamoDB
- Use HTTPS for all communications
- Implement proper error handling and input validation in Lambda functions
Monitoring and Optimization
- Set up CloudWatch dashboards for key metrics
- Configure alarms for critical thresholds (e.g., API errors, Lambda duration)
- Use X-Ray for distributed tracing
- Regularly review and optimize: — Lambda memory/timeout settings — DynamoDB capacity — S3 storage classes
Conclusion
This serverless photo-sharing application demonstrates the power of cloud-native architecture on AWS. It offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and eliminates traditional server management overhead. The combination of managed services provides high availability, automatic scaling, and robust security, making it an ideal solution for modern web applications.
This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by Keyur Modi