This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Reinforcement Technology Advancements
Table of Links
3 Model and 3.1 Associative memories
6 Empirical Results and 6.1 Empirical evaluation of the radius
6.3 Training Vanilla Transformers
7 Conclusion and Acknowledgments
Appendix B. Some Properties of the Energy Functions
Appendix C. Deferred Proofs from Section 5
Appendix D. Transformer Details: Using GPT-2 as an Example
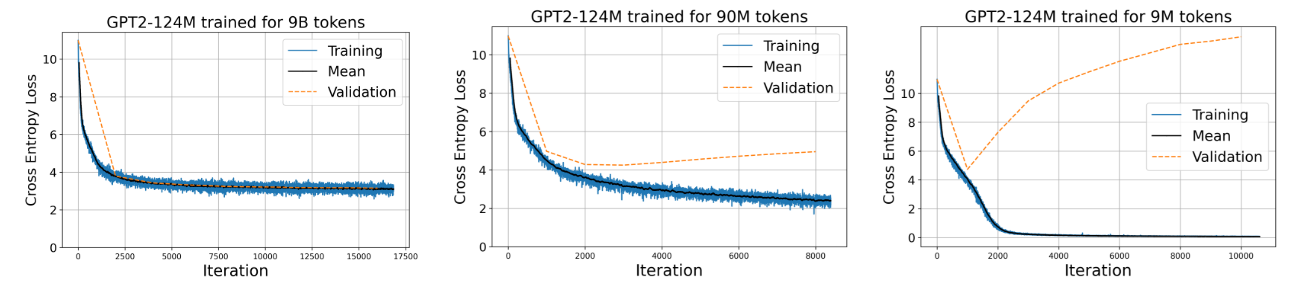
6 Empirical Results
We explore the hypothesis regarding the radius r in Section 5 using a pre-trained GPT-2 medium model. Additionally, we train various GPT-2 small models and vanilla Transformer models to analyze their cross-entropy losses.
6.1 Empirical evaluation of the radius

\
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Xueyan Niu, Theory Laboratory, Central Research Institute, 2012 Laboratories, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.;
(2) Bo Bai baibo (8@huawei.com);
(3) Lei Deng (deng.lei2@huawei.com);
(4) Wei Han (harvey.hanwei@huawei.com).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 DEED license.
:::
1. available at https://github.com/openai/gpt-2
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Reinforcement Technology Advancements