This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by Joseph Ibeh
 Introduction
Introduction
This project demonstrates how to build, containerize, and deploy a simple Flask application with Docker, using GitHub for version control and GitHub Actions for Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD). You will learn how to:
- Create a simple Flask web application.
- Containerize the application using Docker.
- Set up version control with Git and GitHub.
- Implement CI/CD pipelines using GitHub Actions to build and deploy the Docker image.
 Prerequisites
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that you have the following tools installed:
- Python: A programming language for building web applications.
- Flask: A lightweight Python web framework.
- Docker: A platform for developing, shipping, and running applications in containers.
- Git: A version control system for tracking changes in code.
- GitHub: A platform for hosting and sharing code repositories.
- Docker Hub: A cloud-based registry to share Docker images.
If you don’t have these installed, refer to their respective official websites for installation instructions.
 Step 1: Create a Simple Flask Application
Step 1: Create a Simple Flask Application
-
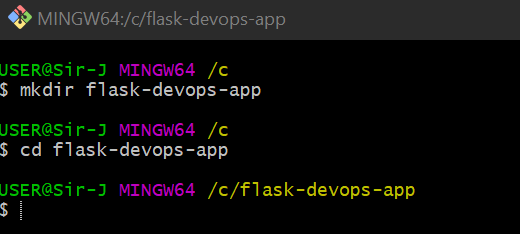
Create a new folder for the project:
mkdir flask-devops-app cd flask-devops-app
-
Set up a Python virtual environment:
python -m venv venv -
Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/Scripts/activate # On Windows use: venv\Scripts\activate -
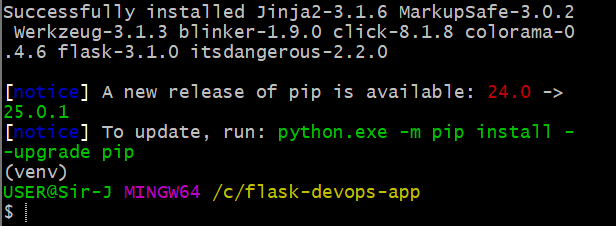
Install Flask:
pip install flask
-
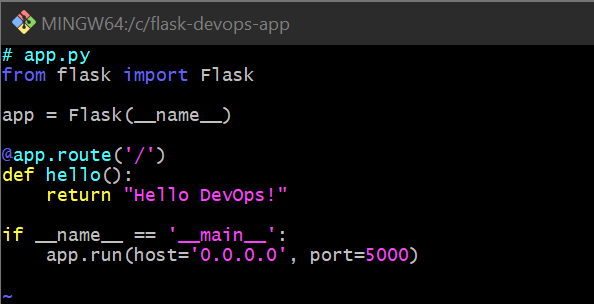
Create the
app.pyfile:
# app.py from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/') def hello(): return "Hello DevOps!" if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
-
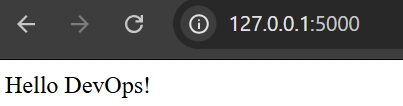
Run the app locally:
python app.py Visit
http://localhost:5000in your browser. You should see"Hello DevOps!".
 Step 2: Containerize the Application
Step 2: Containerize the Application
-
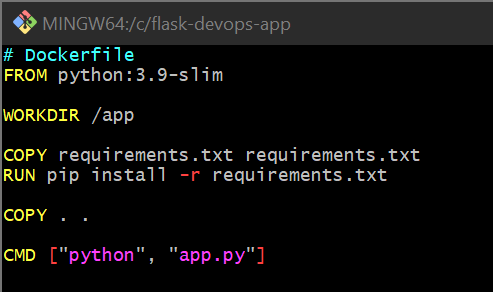
Create a
Dockerfilein the same folder:
# Dockerfile FROM python:3.9-slim WORKDIR /app COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt RUN pip install -r requirements.txt COPY . . CMD ["python", "app.py"]
-
Generate
requirements.txt:
pip freeze > requirements.txt -
Create a
.dockerignorefile:
__pycache__/ *.pyc venv/ -
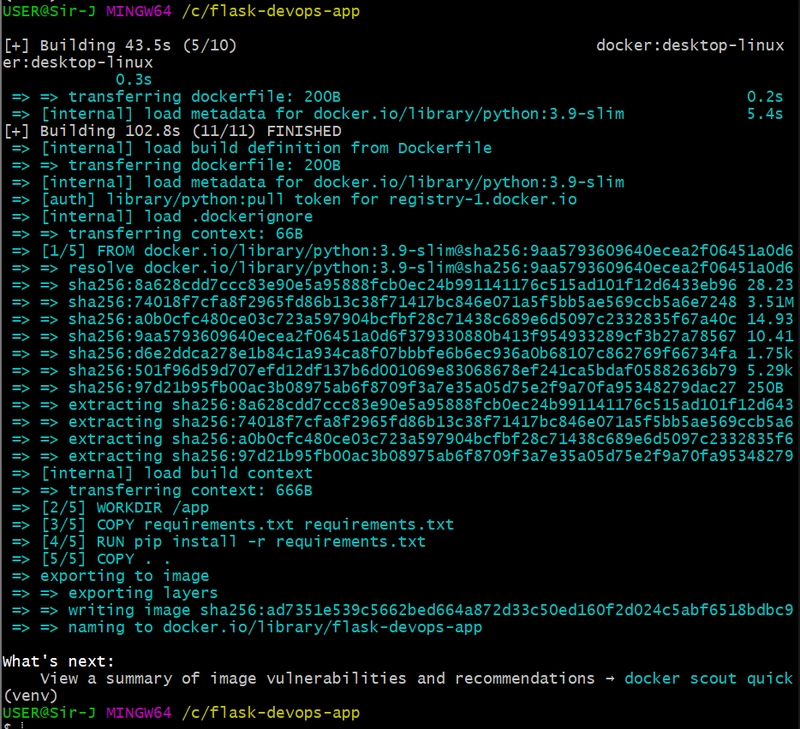
Build the Docker image:
docker build -t flask-devops-app .
-
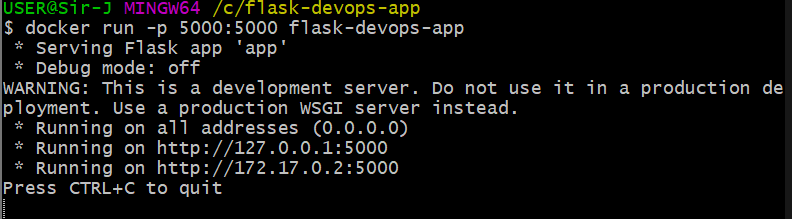
Run the Docker container:
docker run -p 5000:5000 flask-devops-app Open
http://localhost:5000again and see your app running inside a Docker container.
 Step 3: Set Up Version Control
Step 3: Set Up Version Control
 Tools: Git + GitHub
Tools: Git + GitHub
-
Initialize a Git repository:
git init -
Create a
.gitignorefile:
venv/ __pycache__/ *.pyc -
Commit your files:
git add . git commit -m "Initial commit" -
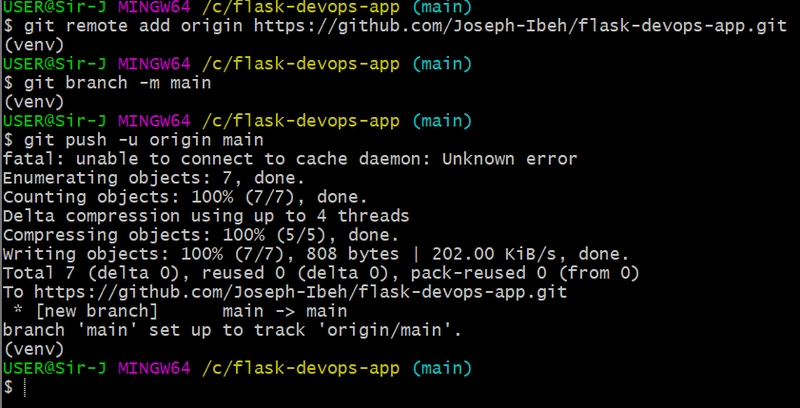
Create a GitHub repository and link it to your local repo:
git remote add origin https://github.com/YOUR_USERNAME/flask-devops-app.git git branch -M main git push -u origin main
 Step 4: Implement CI/CD with GitHub Actions
Step 4: Implement CI/CD with GitHub Actions
 Tools: GitHub Actions, Docker Hub
Tools: GitHub Actions, Docker Hub
-
Create a
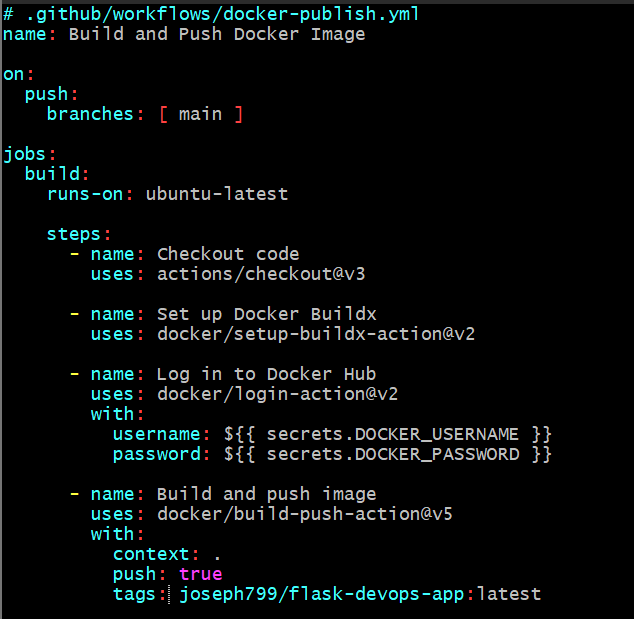
.github/workflows/docker-publish.ymlfile:
mkdir -p .github/workflows touch .github/workflows/docker-publish.yml -
Edit the
docker-publish.ymlfile and add the following content:
# .github/workflows/docker-publish.yml name: Build and Push Docker Image on: push: branches: [ main ] jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v3 - name: Set up Docker Buildx uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2 - name: Log in to Docker Hub uses: docker/login-action@v2 with: username: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_USERNAME }} password: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }} - name: Build and push image uses: docker/build-push-action@v5 with: context: . push: true tags: YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/flask-devops-app:latest
-
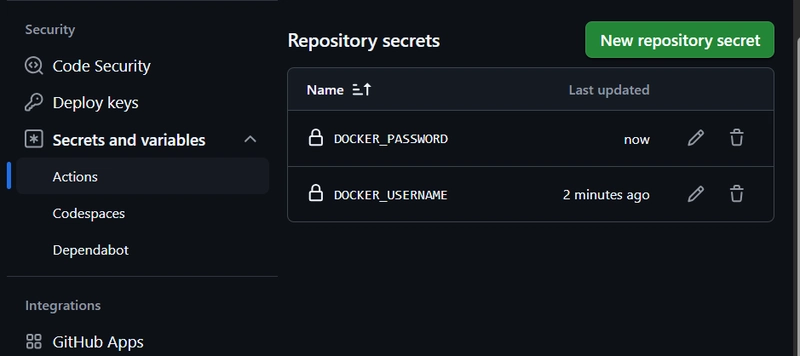
Add Docker Hub credentials as GitHub Secrets:
- Go to your GitHub repository → Settings → Secrets and variables → Actions
- Add the following secrets:
-
DOCKER_USERNAME→ your Docker Hub username -
DOCKER_PASSWORD→ your Docker Hub password or access token
-
-
Push your code again:
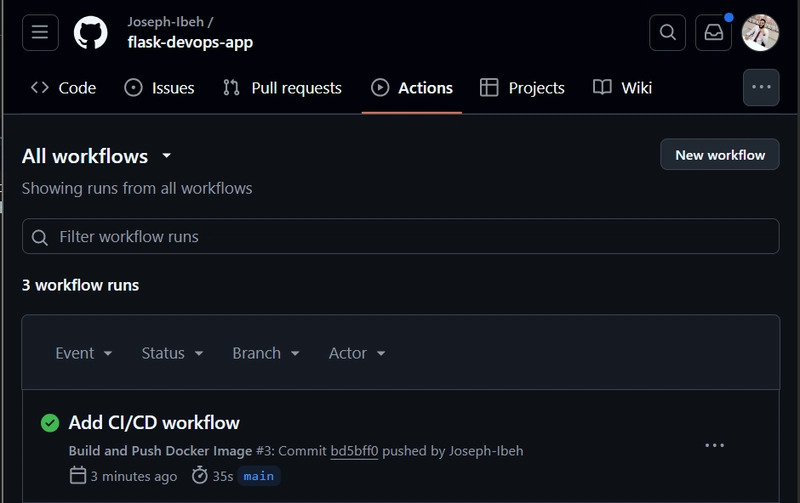
git add . git commit -m "Add CI/CD workflow" git push
GitHub Actions will now automatically build your Docker image and push it to Docker Hub whenever you push to the main branch.
 Final Output
Final Output
 A live Flask app running inside a Docker container.
A live Flask app running inside a Docker container. The source code is hosted on GitHub.
The source code is hosted on GitHub. The Docker image is automatically built and pushed to Docker Hub on every commit.
The Docker image is automatically built and pushed to Docker Hub on every commit.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully created a simple Flask app, containerized it with Docker, set up version control with Git and GitHub, and implemented CI/CD with GitHub Actions. This project is a foundational step in building scalable and automated systems in DevOps.
 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
- If Docker is not running: Ensure Docker Desktop is open and running.
- If you encounter permission issues with GitHub Actions: Double-check your Docker Hub credentials in GitHub Secrets.
- If the Flask app does not load: Ensure you are using the correct port and that the Docker container is running. needs!
This content originally appeared on DEV Community and was authored by Joseph Ibeh